When deciding on the best way to nourish your baby, understanding the breastfeeding vs formula pros and cons can help you make an informed choice. According to experts, breastfeeding is the best way for a baby, as it has many health benefits and many immunity boosters. If you can’t breastfeed, you can try formula feeding your baby instead, which can help to keep the baby healthy and maintain the baby’s nutrition.

In this article, I will explore the breastfeeding vs formula pros and cons in detail. Also offering insights into the benefits and considerations of each method so you can decide what best suits your baby’s needs and your lifestyle.
Table of Contents
Breastfeeding and Formula Feeding in Detail
Breastfeeding
The World Health Organization (WHO) advises mothers to start breastfeeding their newborns within an hour of their delivery and to do so for at least the first six months of the child’s life. Breast milk is the best food option for all infants since it provides a variety of nutrients.
As a responsible mother, you should know breastfeeding vs formula pros and cons. The majority of specialists concur that breastfeeding is the best option for infant nutrition and feeding when compared to formula feeding. However, there are other circumstances in which a mother may need to use formula or add formula to breastfeeding, and both of these methods still give your child enough nutrients. Mothers should talk to their healthcare professional about breastfeeding vs formula pros and cons and drawbacks of each feeding style.

Physiology of Milk Production
The primary mediators of breast milk production are a number of hormones that both directly and indirectly regulate this process. While oxytocin and prolactin have a direct effect on nursing, a number of other hormones, including progesterone and estrogen, have an indirect effect.
Sensory nerves in the breast send this signal to the pituitary gland in the brain when a baby is nursing. While the anterior lobe of this gland is responsible for secreting prolactin, its posterior lobe secretes oxytocin.
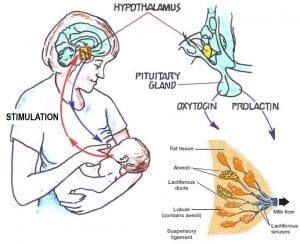
Prolactin
Prolactin levels increase throughout pregnancy to help the mammary tissue grow and mature in preparation for lactation. Notably, milk is not released until after birth, when progesterone and estrogen levels sharply and quickly decline due to the high levels of these hormones during pregnancy.
Prolactin levels will continue to increase during the first few weeks of life as the baby continues to stimulate and suckle the nipple. Because of this, lactation experts frequently advise new moms to nurse every two to three hours to boost their blood levels of prolactin, which will aid in the production of milk.
Oxytocin
The breasts’ alveoli produce milk in response to prolactin stimulation, and the milk is then kept there until elevated oxytocin levels cause the sacs to collapse. Milk can then pass through the alveolar cells and fill ducts, which will eventually transport the milk outside the breast.
Formula Feeding

Breast milk can be substituted with formula. It is created using a unique powdered dry milk. Cow’s milk is used to make the majority of infant formula products, along with additional vitamins and minerals. Vegetable oil fat is also included in the formula.
Breastfeeding vs Formula Pros and Cons

Breastfeeding Advantages
According to research, breastfeeding offers a number of health benefits for both the mother and the child, including increased immunity for the infant and a lower chance of breast cancer for the mother. Infants should, if at all possible, be nursed exclusively for at least six months before switching to breastfeeding with complementary foods for at least the first year, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP).
Breast milk supports a strong immune system and is safe and hygienic, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). It has also been demonstrated that breast milk helps children grow and maintain their health as they get older. Breastfed babies are less likely to suffer from a number of childhood diseases that can persist into adulthood. According to the WHO, children who are breastfed also score higher on intellectual tests.
For at least the first few weeks, a premature baby’s mother’s milk provides more nourishment, and a mother’s breast milk is tailored to the baby’s needs as it develops. Many of the advantages of mother’s milk can also be obtained via donor breast milk.
Breastfeeding may decrease a baby’s risk of these conditions
1. Asthma
2. Celiac disease
3. Leukemia
4. Diabetes
5. Diarrhea
6. Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
7. Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Breastfeeding has advantages for mothers as well. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, breastfeeding reduces a mother’s risk of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, Type 2 diabetes, and high blood pressure. It has also been demonstrated that breastfeeding helps postpartum moms reach a healthy weight.
Breastfeeding Challenges and Breastfeeding Difficulties
Although nursing is the recommended method of feeding babies, there are a number of obstacles that might make breastfeeding difficult or impossible, such as the mother’s health or the baby’s health. Additionally, breastfeeding may result in unpleasant side effects, including mastitis, nipple pain, or fungal infections.
Approximately 70.3% of moms reported nursing issues, and more than 60% of mothers stop breastfeeding early, including cracked nipples, a sense of insufficient milk, soreness, and exhaustion, according to research published in Nutrients. Most of the difficulties happened in the first month.
Because their underdevelopment makes it more difficult for them to synchronize their sucking, swallowing, and breathing movements, premature babies may find breastfeeding challenging. Additionally, their nutritional needs can be greater than those of breast milk. In these situations, the doctor may advise exclusive formula feeding or augmenting breast milk with preemie formula.

Reasons 60% of mothers stop breastfeeding early
1. Cracked nipples
2. Sense of insufficient milk
3. Concern about taking medication while breastfeeding
4. Cultural pressures and lack of family support
5. Infant nutrition and weight concerns
6. Lack of parental leave and unsupportive work policies
7. Lactation and latching issues
8. Unsupportive hospital policies and practices
Breastfeeding mothers should not take some drugs. For instance, mothers undergoing chemotherapy are not allowed to breastfeed. In order to ensure that breastfeeding is safe, be important to let your doctor know if you are taking any drugs. A medication database for breastfeeding safety is available from the National Library of Medicine.
Low milk production, engorged breasts, clogged milk ducts, exhaustion, a significant time commitment, depressive or melancholy feelings, and coping with the criticism of those who might not be in favor of breastfeeding are additional difficulties. Consult your healthcare practitioner for assistance, or review the Office on Women’s Health’s resources for information on common issues and solutions.
Formula Advantages
Convenience and the ability to customize nutrition for each baby are key benefits when considering breastfeeding vs formula pros and cons. Additionally, formula offers a substitute for nursing in the event that a healthcare professional advises against it. For babies with special needs, there are formulas that are hypoallergenic and lactose-free.
Formula is an option for mothers who must stop nursing because of medical conditions, drugs, or surgery. Preemies who use baby formula may also benefit from catch-up growth. Additionally, in the breastfeeding vs formula pros and cons discussion, formula feeding can be a critical choice for preemies, as studies show that specially formulated preemie formulas support short-term growth and weight gain.
Top 4 formula advantages
1. Either parent or caregiver can feed. This gives mothers a chance to rest and allows other loved ones to bond with their child and share feeding duties.
2. Less frequent feeding times. Breast milk digests more quickly, which also means babies get hungry faster. Formula can keep your child full for longer.
3. Various formula types. If your baby has special feeding needs, such as an allergy or sensitivity, there are formulas available that cover the spectrum.
4. Formula is convenient and does not require refrigeration before mixing. This reduces preparation time and gives you more flexibility to pack the diaper bag the night before and rush less in the mornings.
5. All the benefits, less of the not-so-fun. Breastfeeding is a natural and wonderful bonding experience. Though the payoff is priceless, a certain amount of non-fun things come with the territory that’s skipped in formula feeding. Some examples include engorgement, teething, finding a private area (if desired), effects on certain body parts, and more.
Baby formula is still a nutritionally balanced way to feed your child, even though breastfeeding is the recommended option.The FDA’s nutritional requirements must be followed by all commercial formulas sold in the United States.
Tips for choosing a baby formula
1. If your infant is healthy, full-term, and not nursing, you should start with a formula made from cow’s milk before experimenting with other kinds.
2. A formula’s cost does not necessarily indicate its quality. Formula firms utilize terms like “gold” or “superior” to entice parents to purchase their product. Decide on what you can afford.
3. Examine the number of scoops required to prepare a feed. This can help you estimate the potential shelf life of a tin of formula.
4. Make sure you’re selecting the appropriate formula for your baby’s age by reading the label.
5. Take a look at the protein content of the formula. Your baby may be more likely to grow up to be overweight or obese if they consume too much protein.
6. Allow a few days for your baby to adjust to a new formula type. Don’t change brands too much.
7. Before choosing baby formula understand about breastfeeding vs formula pros and cons in details.
Formula Disadvantages
Baby formula disadvantages may include its cost, inability to provide nutrition, antibodies, and immunosupport to babies, and baby formula side effects.
The cost of formula feeding is high. The annual cost might range from $800 to $2,800. Inflation may cause this number to increase. Hospital-given brand-name formulas can cost up to 66% more than store-brand alternatives, but women are more likely to continue using the brand they are familiar with. Due to formula shortages, baby formula recalls may also result in additional stress.
Unbreastfed babies lose out on the special advantages breast milk provides for their immune and cognitive development. This includes the health benefits of breast milk, such as antibodies. Furthermore, although the adverse effects of baby formula are usually restricted to minor digestive problems, there are some health hazards that could be fatal.
Frequently asked questions?
How is formula different from cow’s milk?
After your baby is six months old, you can start adding little amounts of cow’s milk to their meals.
How is formula different from breast milk?
Breast milk has antibodies that help shield your infant from disease, which is one of the primary distinctions between it and formula. Your infant’s immune system is not fully formed at birth.
Breast milk automatically adjusts its composition to meet your baby’s needs. As your infant gets older, you can purchase different varieties of formula milk, but the ingredients remain the same.
Additionally, formula milk contains more protein than breast milk.
Why might I give my baby formula?
1. be incapable of producing enough breast milk to meet your infant’s requirements
2. are unable to breastfeed because of a medical condition or medication.
3. not always be with your child, for example, if you are returning to work.
4. unable to breastfeed, such as fathers, transgender or non-binary parents, adoptive or foster parents, or kinship caregivers.
5. if you have suffered from sexual abuse or another form of trauma involving your breasts, in which case you decide to use formula to feed your child, decide not to breastfeed for another reason, or cease breastfeeding before the child is 12 months old.
What are the different types of formula?
There are several ways that formula is manufactured:
1. milk-based formulas — based on cow’s milk
2. soy-based formulas — based on soybeans.
3. specialty formulas — produced from “predigested” cow’s milk, in which the protein has been eliminated, broken down, or reduced. There are other hypoallergenic formulations available.
4. added compounds — may consist of antioxidants, long chain polyunsaturated (LCP) acids, probiotics, and prebiotics. These, according to the formula’s makers, make it more resemble breast milk. This does not, however, imply that your infant can process these substances in the same manner as if they were nursed.
How can I tell when my baby is hungry?
When a baby is hungry, they typically cry. They will get calm and begin sucking if you put the bottle’s teat in their mouth.
As you would when nursing, try to hold your baby in your arms. Hold them close, gaze into their eyes, and listen for any signs or clues they may give you.
How to prepare formula?
1. Examine the container’s information.
2. Verify how many scoops of powder and water you’ll need to blend.
3. Thoroughly wash and pat dry your hands.
4. Make sure the bottle you’re using is clean and sterile.
5. Make sure your workspace is clear and uncluttered.
Is breastfeeding really better for babies than formula?
Conclusion
choosing between breastfeeding and formula feeding is a personal decision that depends on a variety of factors, including your baby’s needs, your health, lifestyle, and support system. Understanding the breastfeeding vs formula pros and cons can help you make an informed choice that’s best suited for both you and your baby. While breastfeeding provides unmatched health benefits and immune support, formula feeding offers flexibility and can still provide complete nutrition. Ultimately, whether you choose breastfeeding, formula, or a combination of both, the goal is to ensure your baby receives the nourishment they need to grow and thrive. By considering the breastfeeding vs formula pros and cons, you can confidently select the approach that works best for your family’s unique situation.

































6 thoughts on “Breastfeeding vs Formula Pros and Cons”